Cloud explained: AWS Cloud structure
This is the introductory write up about cloud. We will focus on the AWS as an example for the introduction to the cloud concepts and terms in this series. It will be in series and we will go through an article about different segments of the AWS cloud concepts and services.
AWS fundamental concepts
Fundamental blocks of the AWS or any public cloud provider are:
- Availability zone
- Region
- Edge location
- Latency
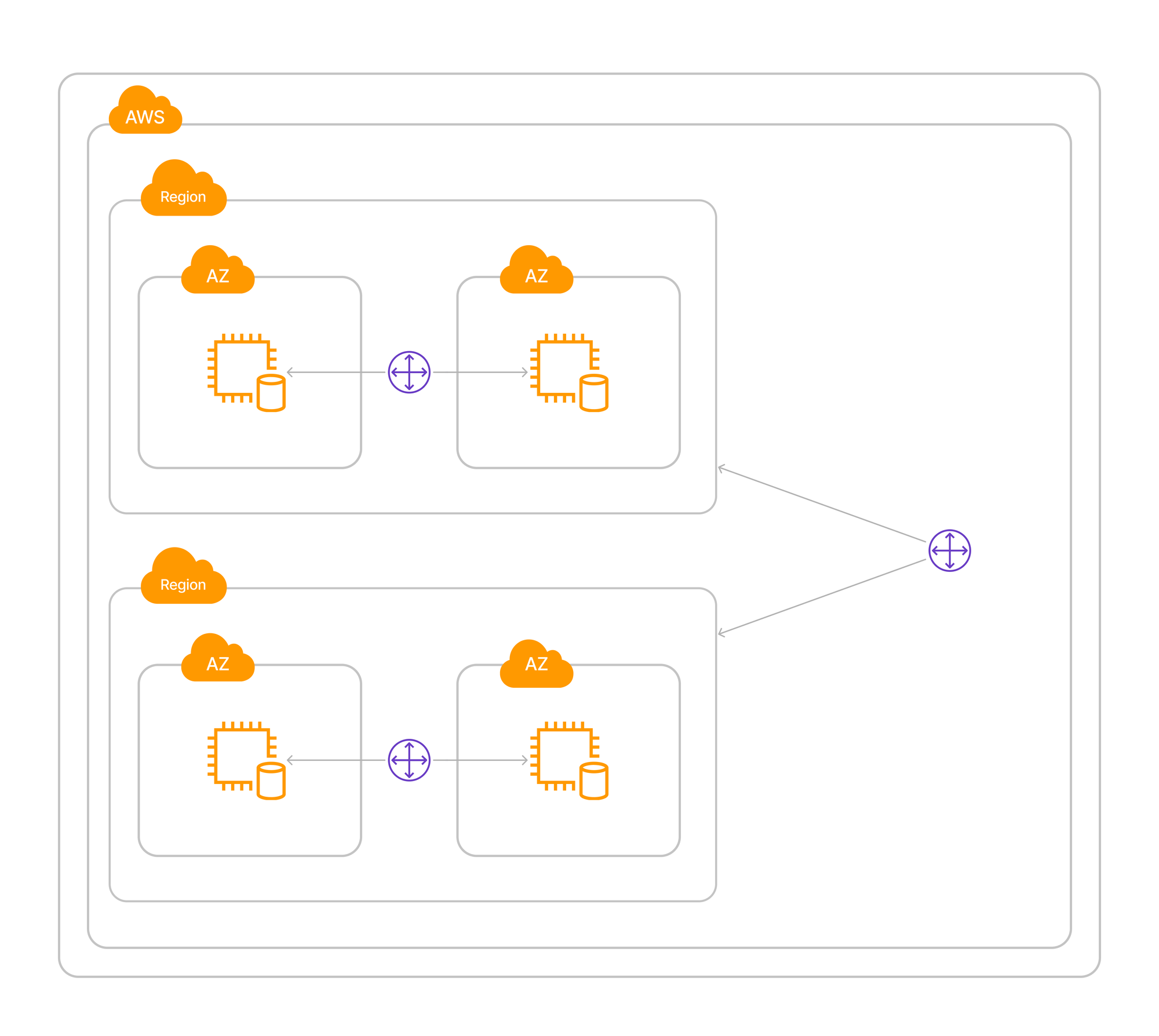
Availability zone
Availability zone represents one/or more data centers in isolated geographical location from other Availability zones. It is physical part of the cloud. Data center or more in one isolated location.
Region
Region is set of Availability zones connected via low latency links. Low latency means - very large speed of data transfer between data centers.
Edge location
Edge location is a data center geographically closer to the end-user. This way the physical distance is smaller to the intended audience thus lower latency - bigger speed of data transfer.
Latency
Latency is metric for the delay of time between sending request and starting to receive data.
Cloud business models
There three main categories of services provided from public cloud provider - business related.
Infrastructure as a service
A model in which customer gets the virtual resources where the customer takes over the responsibility of installing software and configuring everything. Example would be virtual machine.
Platform as a service
A model in which customer gets the platform where he/she can create and run custom software. Example would be Kubernetes.
Software as a service
A model in which customer gets complete software that is paid by usage. This model most often uses subscription (monthly/yearly) and provides access to software only to members. Example would be Gmail.
Types of cloud
There are three types of cloud:
- Public
- Hybrid
- On premise
Public
Public cloud is provided by biggest companies in the world. Three major players are Azure, AWS, and GCP. The services are provided to the users on the public internet. Data is stored on the data centers used by the public cloud provider not on the local machines by the customer. This raises questions about security and confidentiality of the data.
Hybrid
Hybrid cloud is a mix of the public and on-premises cloud. This type of cloud usually is designed so that the customer's confidential data doesn't leave the on-premises cloud, and noncritical components of customer's business are using the public cloud. Usually in hybrid model on-premises and public clouds are connected via VPN
On premise
On premise cloud is the type of cloud which is hosted by the customer in local facilities. Customer owns the hardware and handles everything by themselves. Larger companies prefer on premise for critical data and operations.